Cyprus Energy Sector: Renewable Transitions and Independence
The energy landscape in Cyprus is undergoing a profound transformation. Traditionally dependent on imported fossil fuels, the island nation is now steering its energy sector Cyprus towards renewables and energy independence Cyprus. This strategic shift is motivated by geopolitical challenges, economic concerns, and environmental commitments. By exploring the evolution of the oil and gas Cyprus industry, alongside the rise of renewable energy Cyprus, one can better understand how Cyprus aims to secure a sustainable and autonomous energy future.
Cyprus’s geographic position in the Eastern Mediterranean presents unique opportunities and challenges. Historically reliant on imported oil and gas, the country has faced vulnerability to external supply shocks and price fluctuations. Modernizing infrastructure and diversifying energy sources have become priorities within the broader energy policy framework.
The Historical Context of the Energy Sector Cyprus
For decades, the backbone of Cyprus’s energy sector was fossil fuels, predominantly oil and gas imports. Due to limited domestic hydrocarbon resources, the island imported almost all of its energy needs, making it dependent on fluctuating global markets. The isolated nature of the country’s electrical grid underscored the importance of energy security and affordability for households and industry.
The discovery of offshore natural gas reserves in Cypriot waters marked a turning point in the oil and gas Cyprus narrative. These reserves promised not only an economic boost but also a potential pathway to reducing the island’s reliance on imports. However, geopolitical tensions and territorial disputes in the Eastern Mediterranean have complicated the extraction and use of these resources.
Reliable energy is fundamental to national security, and Cyprus has historically depended on external sources, underscoring its vulnerability.
Despite these challenges, state-led efforts to develop domestic energy infrastructure and diversify suppliers have gradually improved the energy outlook, laying groundwork for current renewable energy ambitions.
The Rise of Renewable Energy Cyprus
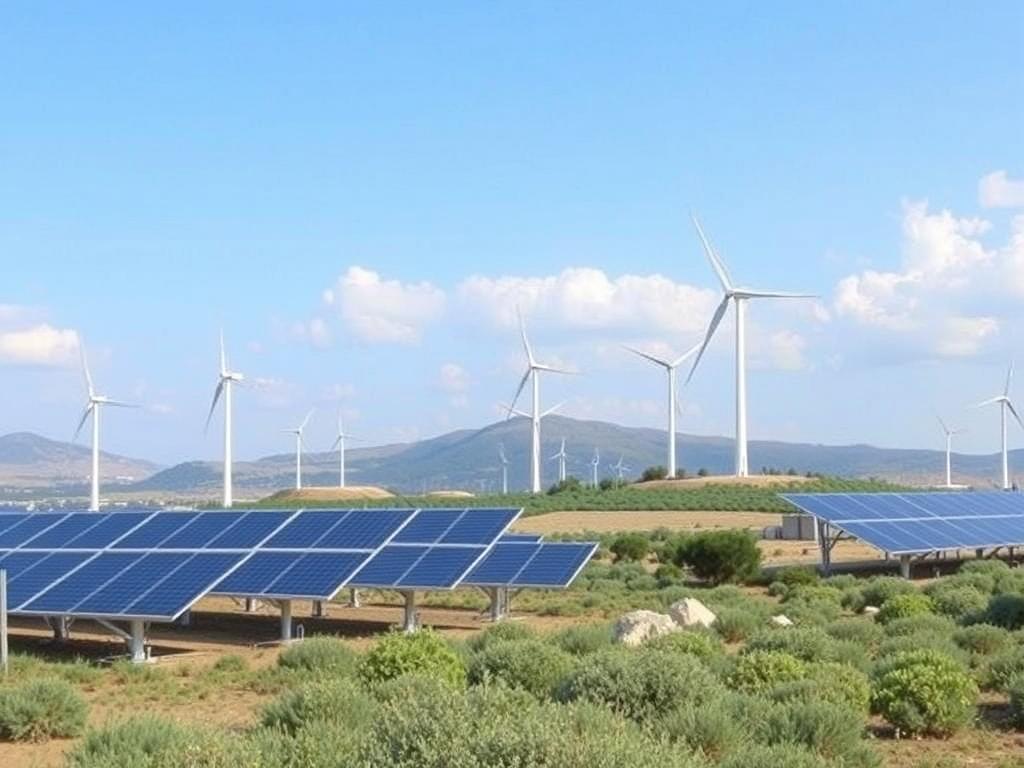
The transition to renewable energy Cyprus is not just an environmental imperative but a technological and economic opportunity. Harnessing the island’s abundant solar and wind resources, alongside emerging technologies, is reshaping the energy sector Cyprus towards sustainability and resilience.
Cyprus benefits from over 300 days of sunshine annually, making solar power the most promising renewable source. The solar photovoltaic (PV) installations, both at utility scale and distributed across households and businesses, have seen a sharp rise in capacity. Wind power, while more limited due to geographic and climatic factors, contributes meaningfully in selected regions.
Government policies have accelerated this shift through incentives, feed-in tariffs, and regulatory reforms designed to attract investment and reduce bureaucratic hurdles. These measures align with broader European Union directives mandating increased renewable penetration and carbon reductions.
The island’s natural advantages in solar irradiation position it uniquely to lead in renewable energy innovation in the Mediterranean.
Investment in renewable energy Cyprus now encompasses emerging technologies such as energy storage systems, smart grid enhancements, and hybrid solutions combining renewables with imported LNG.
Renewable Energy Capacity and Targets
Cyprus has set ambitious goals to reach at least 23% of total energy consumption from renewable sources by 2030, in line with EU climate policies. This requires sustained expansion of solar PV, wind farms, and bioenergy projects. Energy efficiency measures and demand-side management are integral to these efforts.
| Renewable Source | Installed Capacity (MW, 2023) | Target Capacity (MW, 2030) |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Photovoltaic (PV) | 180 | 400 |
| Wind Energy | 55 | 100 |
| Bioenergy & Others | 10 | 25 |
These targets demonstrate the government’s commitment to rapidly scaling renewable energy Cyprus, reducing carbon emissions, and fostering energy independence Cyprus.
Oil and Gas Cyprus: Prospects and Challenges
The offshore oil and gas Cyprus sector holds strategic importance but also introduces complexity to the island’s energy strategy. Hydrocarbon exploration within Cyprus’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) has revealed significant natural gas fields, the most prominent being the Aphrodite field. These reserves inject new dynamics into the energy independence Cyprus discussion.
Despite the potential, extracting and monetizing these resources requires substantial investment and cooperation. Geopolitical disputes with neighboring countries over maritime boundaries pose risks to development timelines and project feasibility. Environmental concerns and fluctuating global oil and gas prices also influence investment decisions.
Cyprus’s hydrocarbon potential offers hope for energy independence but also presents geopolitical and environmental challenges that must be deftly managed.
To navigate these complexities, Cyprus is collaborating with international energy firms and pursuing regional partnerships aimed at resource development and export infrastructure. Plans to connect natural gas supplies to Europe via pipelines or liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminals could strengthen both economic and energy ties.
Oil and Gas Exploration Timeline and Developments
Following initial licensing rounds between 2011 and 2018, several multinational companies initiated exploratory drilling with mixed results. While the Aphrodite field contains commercially viable reserves, other exploration wells have faced delays and cancellations.
The government continues to update its regulatory frameworks to encourage responsible development and attract new investment amid global shifts toward decarbonization. Balancing oil and gas Cyprus with renewable energy Cyprus is a delicate exercise but essential for transitional energy strategies.
The Quest for Energy Independence Cyprus
Energy independence Cyprus is an overarching goal driving policy, infrastructure investment, and innovation. Reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels enhances national security, stabilizes the economy, and complements environmental goals simultaneously.
Achieving energy independence involves integrating renewable energy sources, maximizing domestic resource utilization, and improving energy efficiency. Cyprus has also invested in interconnectivity projects such as the EuroAsia Interconnector, which links electricity grids of Cyprus, Greece, and Israel. This connection not only stabilizes local supply but also opens opportunities for energy trade and grid balancing.
Energy independence Cyprus reinforces sovereignty and resilience, lessening vulnerability to external political and economic pressures.
Moreover, decentralizing energy production through distributed renewable generation empowers local communities and business sectors while reducing transmission losses and grid stress.
Strategies to Enhance Energy Independence
- Scaling renewable energy installations, especially solar PV systems.
- Developing energy storage solutions to mitigate intermittency.
- Leveraging natural gas reserves responsibly as a transition fuel.
- Advancing grid interconnection to neighboring countries.
- Implementing energy efficiency programs and demand management.
These combined strategies align with national policy objectives and European Union directives, positioning Cyprus as a forward-looking energy actor in the region.
Challenges and Future Outlook of Cyprus Energy Sector
Despite clear progress, the energy sector Cyprus faces hurdles in technology integration, financing, and regulatory environment adjustment. High initial costs for renewables and storage, coupled with infrastructural limitations, slow down the pace of overall transition.
Geopolitical tensions in the Eastern Mediterranean affect project security and cooperation. Navigating these challenges requires diplomatic finesse and multilateral engagement. Additionally, the transformation demands workforce upskilling and public acceptance of new energy technologies.
The path to a renewable, independent energy future in Cyprus is complex but holds the key to long-term economic and environmental stability.
Emerging technological advances such as green hydrogen production and enhanced energy management systems could further propel Cyprus’s energy sector. Government commitment and private sector participation will remain critical to realize these ambitions over the next decades.
Empowering Cyprus’s Energy Future: Independence through Innovation
Cyprus’s journey to reshape its energy sector reflects a broader global narrative of balancing energy security, economic growth, and environmental stewardship. The island’s transition from dependency on imported oil and gas towards renewable energy Cyprus embodies resilience and forward-thinking.
The intertwining of offshore hydrocarbon potential with a steadfast expansion of solar and wind power reveals a pragmatic approach. Cyprus neither dismisses the value of its oil and gas resources nor foregoes its urgency to embrace renewables. This hybrid strategy increases energy independence Cyprus and nurtures sectoral innovation.
Investment in infrastructure, regulatory reform, and regional partnerships are pivotal. By harnessing its natural solar advantage, developing energy storage capacities, and constructing grid interconnectors, Cyprus enhances its energy autonomy. Moreover, integrating global best practices and technologies strengthens both public and private sector capabilities.
The story of Cyprus’s energy sector is one of transformation driven by necessity and opportunity. As the island navigates complex geopolitical waters and rapid technological changes, its evolving energy policy serves as a valuable case study in sustainable development and strategic independence within a geopolitically sensitive region.
The future of Cyprus’s energy sector lies in innovation, collaboration, and determination to achieve true energy independence.
This ongoing transition is poised to provide Cyprus not only with a cleaner and more stable energy system but also with economic growth, enhanced security, and leadership in sustainable energy within the Mediterranean region.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the current reliance of Cyprus on imported energy?
Cyprus imports around 90% of its energy needs, primarily in the form of oil and natural gas. - How significant are Cyprus’s renewable energy resources?
Cyprus has abundant solar potential, with over 300 sunny days per year, making solar energy the most significant renewable source. Wind energy also contributes regionally. - What challenges does Cyprus face in exploiting its offshore oil and gas reserves?
Geopolitical disputes, high development costs, and environmental considerations complicate resource extraction and monetization. - How does the EuroAsia Interconnector project impact Cyprus’s energy sector?
It links Cyprus’s electrical grid to neighboring countries, improving supply security, enabling trade, and supporting renewable integration. - What are Cyprus’s renewable energy targets for 2030?
The goal is to achieve at least 23% of total energy from renewable sources, primarily through expanding solar PV and wind capacity. - Is energy independence Cyprus achievable in the near future?
While full independence is challenging, incremental progress through renewables, local resources, efficiency, and interconnections is steadily advancing. - How is Cyprus balancing fossil fuels with renewable energy?
Cyprus pursues a hybrid strategy that utilizes offshore natural gas as a transition fuel while aggressively expanding renewable capacity.